Access control plays a critical role in maintaining security within information technology environments. It regulates who can view or use resources in a computing environment, thereby protecting sensitive data from unauthorized access. Implementing effective access control mechanisms is essential for safeguarding information integrity and confidentiality, and it is a fundamental component of robust cyber security strategies.
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
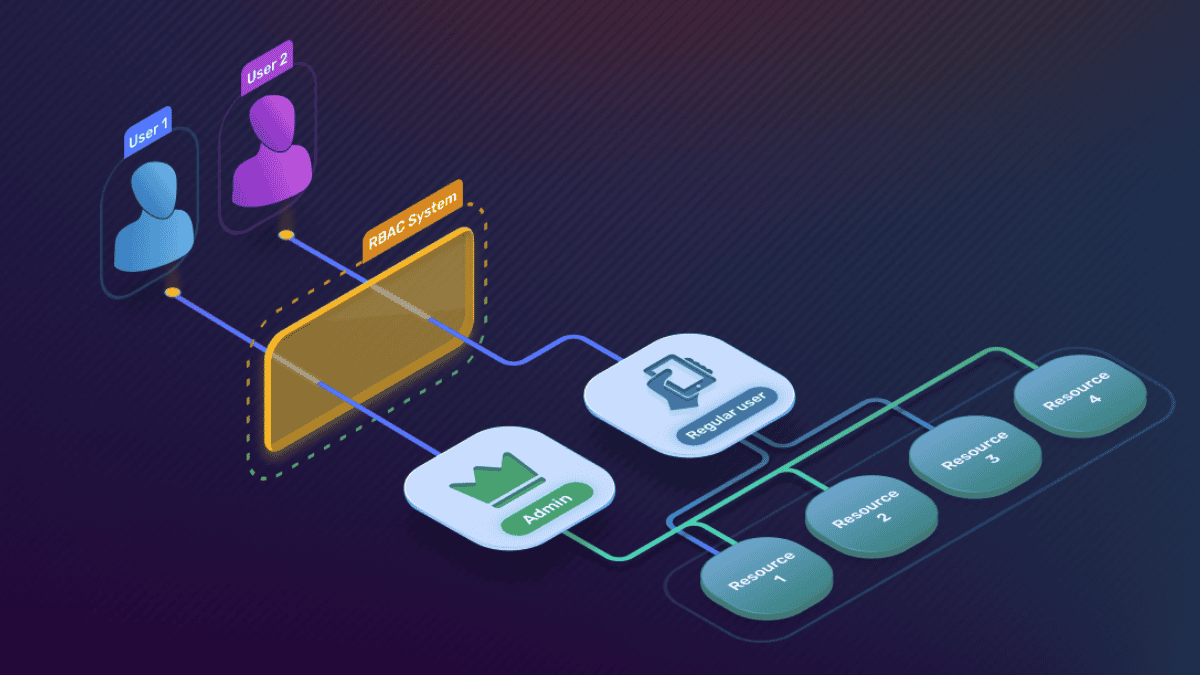
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) is an access management methodology that assigns permissions to users based on their role within an organization. The primary principle of RBAC is the principle of least privilege, where users receive only the necessary access rights required to perform their job functions.
Roles in an RBAC system encapsulate a set of permissions that are linked to specific job functions within the organization. Users are assigned to these roles, which simplifies the management of access rights. The process of granting or revoking access becomes more streamlined, making it easier for organizations to maintain security compliance.
Implementation of RBAC
Implementing RBAC involves several key steps:
- Role Definition: Identify the various roles within the organization, such as administrator, manager, and employee.
- Permission Assignment: Determine which permissions are required for each role. This includes access to specific resources, data, and systems.
- User Role Assignment: Designate users to appropriate roles in alignment with their specific job duties and areas of responsibility.
- Policy Management: Develop and manage access policies to ensure that users have the appropriate permissions as they change roles or responsibilities.
Advantages and Limitations of RBAC
RBAC has several advantages and limitations that organizations must consider:
| Advantages | Limitations |
| Simplifies access management | Can become complex with many roles |
| Enhances security through least privilege | Inflexible for dynamic access requirements |
| Ensures compliance with regulations | Limited granularity in access control |
| Easy to understand and implement | Role explosion may lead to inefficiencies |
RBAC is a widely used access control model that offers a clear structure for managing user permissions based on defined roles. However, organizations must weigh its benefits against potential drawbacks, especially in dynamic environments with diverse access needs.
Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC)
ABAC is a dynamic access control model that provides security based on attributes. These attributes can pertain to the user, the resource being accessed, and the environment in which the access is being requested. This model allows for more nuanced and context-aware access permissions compared to traditional methods.
Definition and Principles of ABAC
The core principle of ABAC is that access rights are granted not just on user roles but also on various attributes. Attributes can be:
- User Attributes: Characteristics or properties of the user, such as job title, department, or clearance level.
- Resource Attributes: Information about the resource, such as the sensitivity of the data or the type of document.
- Environmental Attributes: Contextual variables, like time of day or location from which access is being requested.
This model allows organizations to implement complex access rules based on conditions that consider the unique context surrounding each access request.
Implementation of ABAC
Implementing ABAC requires a structure to manage and evaluate the numerous attributes involved. The process typically includes:
- Define Attributes: Identify the relevant user, resource, and environmental attributes necessary for access control.
- Create Policies: Develop access control policies that outline the conditions for granting access based on specific attribute combinations.
- Deploy ABAC System: Integrate an access control system that can evaluate these attributes in real-time at the point of access.
- Continuous Monitoring: Regularly review and adjust policies and attributes as necessary to align with organizational goals and compliance requirements.
Advantages and Limitations of ABAC
ABAC has several advantages and limitations that organizations should consider.
Advantages
- Granular Control: ABAC allows for fine-grained access control policies, enabling organizations to enforce specific rules tailored to various contexts.
- Dynamic Access: The ability to evaluate access requests based on real-time attributes can enhance security, especially in environments that change frequently.
- Scalability: Suitable for complex organizations with diverse permissions and access needs, as it scales effectively without the need for constant role reassignment.
Limitations
- Complexity: The implementation of ABAC can be more complicated than traditional role-based systems due to the need to manage multiple attributes and policies.
- Overhead: Calculating attribute-based permissions dynamically may introduce performance overhead, impacting system responsiveness.
- Policy Management: Creating and maintaining comprehensive attribute policies can be resource-intensive and may require specialized knowledge.
This comparison highlights the distinct characteristics of the ABAC model within the broader context of access control solutions. By understanding its principles, implementation strategies, and trade-offs, organizations can make informed decisions about adopting ABAC as part of their security framework.
Comparison of RBAC and ABAC
Access control models are essential for managing user permissions and ensuring data security. Understanding the differences between Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) and Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC) helps organizations determine which model best fits their needs.
Flexibility and Scalability
RBAC is based on predefined roles within an organization. While it offers a structured way to manage access, it can become rigid when new roles are needed or existing roles require modifications. Adding new roles may involve significant administrative effort.
ABAC provides more flexibility because it considers various attributes of users, resources, and environmental conditions. Changes in access requirements can be handled dynamically, allowing for easier scalability. Organizations can adapt their access controls without the need for extensive reconfiguration.
Granularity of Access Control
RBAC typically grants access based on roles defined by job functions. This can lead to overly broad access permissions, where users may receive access to data not relevant to their role.
In contrast, ABAC allows for fine-grained access control by utilizing specific attributes such as user location, time of access, and data sensitivity. This granularity enables more precise management of permissions, aligning access rights closely with organizational policies.
Dynamic vs Static Access Control Rules
RBAC access rules are generally static, meaning they are predefined and do not change unless manually updated. This static nature can be limiting in environments where user roles and access needs frequently change.
ABAC supports dynamic access control rules. Decisions can be based on current conditions and attributes that can evolve in real time. This adaptability is beneficial in scenarios where user context changes regularly, such as remote working or fluctuating project requirements.
Comparing RBAC and ABAC across these dimensions, organizations can better understand how each model aligns with their access control needs and make informed decisions regarding their IT security strategies. Just as choosing the right access control model helps mitigate internal risks, it's equally important to recognize external threats—our article How Phishing Bypasses Spam Filters (And Why You Should Care) explores one such critical vulnerability.

Streamline. Strengthen. Scale. LK Tech.
Both scenarios illustrate how the appropriate access control model can be applied effectively based on the organization’s requirements and system design. Choosing between RBAC and ABAC depends on how dynamic or structured your access control needs are. At LK Tech, we offer top-notch IT support tailored to your unique needs, helping businesses implement secure, scalable, and efficient access control solutions. For expert guidance and reliable IT services in Cincinnati, we’re here to help you optimize your systems. Contact us today to discuss how we can elevate your security infrastructure.


